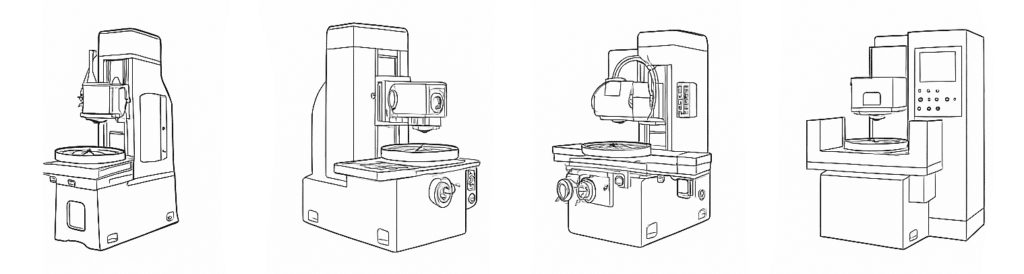
Swisher Finishing Systems
Rotary Grinding Machines
Swisher Finishing Systems carries a legacy that goes beyond machines. For over 90 years, we’ve delivered rotary grinding solutions that withstand the test of time, rebuild after rebuild, challenge after challenge. If it’s worth grinding, it’s worth grinding with a Swisher.
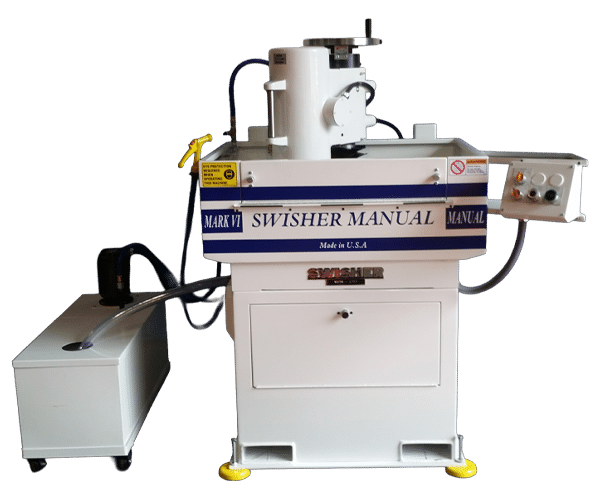
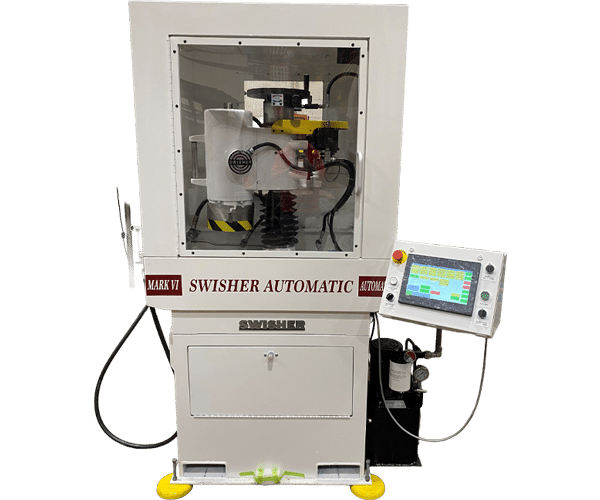
From servo-driven precision models to operator-friendly manual machines, our range includes options for every production need and tolerance requirement. Whether you’re seeking tight repeatability, hands-on control, or high-volume automated throughput, each machine is purpose-built to handle the demands of modern surface grinding. Horizontal Double Disk Manual and Automatic machines are available on a custom-build basis to meet specific application needs.
|
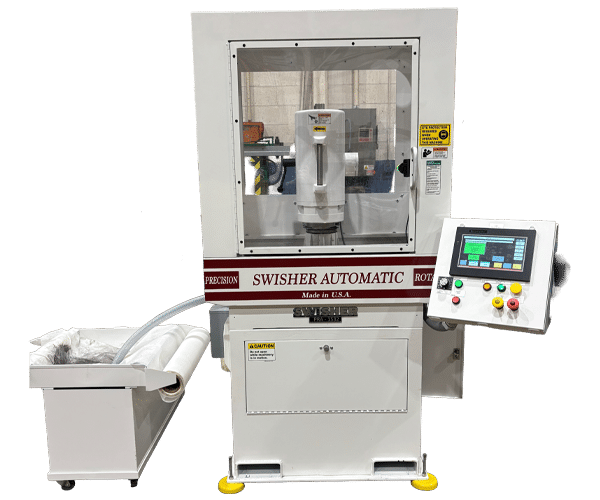
PRECISION ROTARY AUTOMATIC (PRA)
|
|
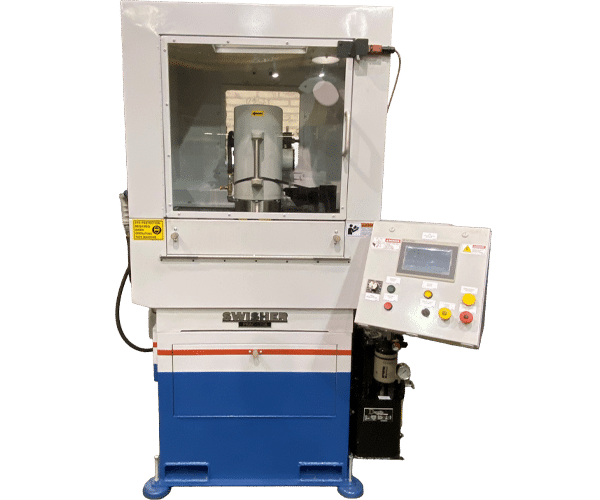
PRECISION ROTARY AUTOMATIC CYCLE (PRAC)
|
|
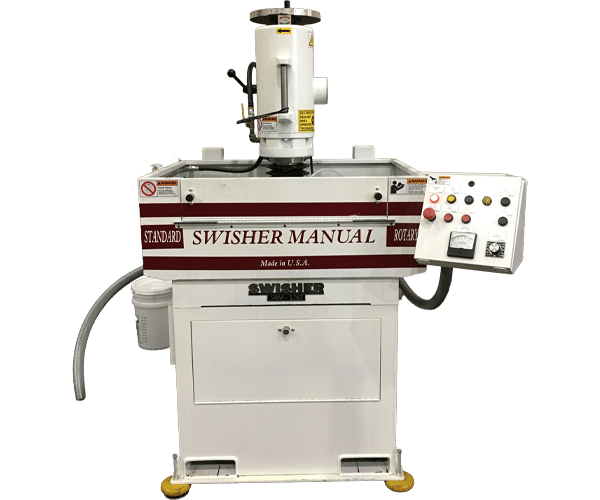
STANDARD ROTARY MANUAL (SRM)
|
|
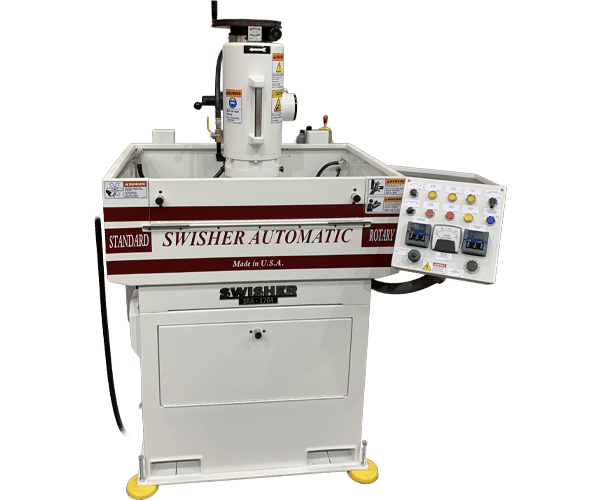
STANDARD ROTARY AUTOMATIC (SRA)
|
|
MARK 6 MANUAL (MVIM)
|
|
MARK 6 AUTOMATIC (MVIA)
|
Swisher grinders are known to operate for decades. Why? Because they were built that way. Our machines are rugged, rebuildable, and respected across industries. Integrated with the engineering strength of Crankshaft Machine Group, Swisher brings:
- In-house test grinding for validation
- Custom design & build capabilities
- Full turn-key systems for surface finishing
- Close-tolerance sizing solutions
- Single- or multi-part grinding flexibility
- Media compatibility: vitrified, CBN, diamond, milling cutters
Horizontal Double Disk Grinders
Swisher’s horizontal double disk grinders are purpose-built for high-production, close-tolerance grinding of complex or difficult parts. Available in both manual and automatic configurations, these machines feature independent infeed, robust 7.5 HP spindles (with optional 0–3600 RPM capability), integrated coolant systems, and a range of customizable fixtures and process automation options. Contact us to discuss your project
Introduction to Rotary Grinding Machines
Rotary grinding machines—also called rotary surface or Blanchard grinders—are vital tools in precision manufacturing. These machines use a rotating abrasive wheel to deliver smooth, flat surfaces with extreme accuracy. Originally revolutionized by Frank J. Blanchard in 1909, vertical spindle rotary surface grinders introduced a new standard for large-part finishing.
Today, rotary grinding machines play a crucial role in modern manufacturing, offering unparalleled accuracy and consistency in material removal. Their importance has only grown with the increasing demand for high-precision components in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics.
The development of rotary grinding machines has been closely tied to the advancement of manufacturing technology:
- 1909: Frank J. Blanchard invents the vertical spindle rotary surface grinder
- 1920s-1930s: Widespread adoption in automotive and machine tool industries
- 1950s-1960s: Introduction of hydraulic controls for improved precision
- 1970s-1980s: Integration of computer numerical control (CNC) systems
- 1990s-present: Advancements in abrasive materials and process monitoring
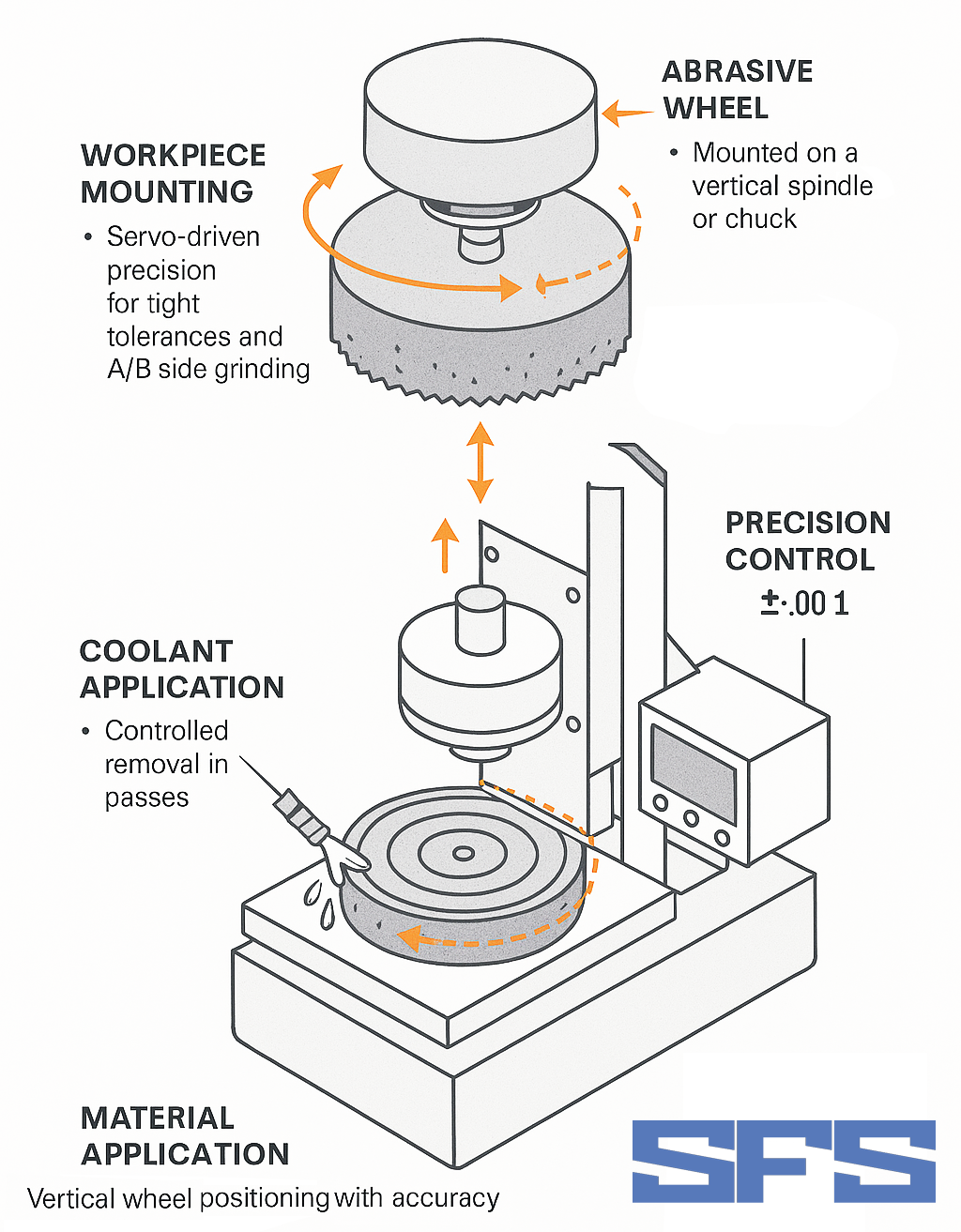
How Rotary Grinding Machines Work
Rotary grinding machines operate on a simple yet effective principle:
- Workpiece Mounting: Secured to a rotating magnetic table or chuck
- Abrasive Wheel: Mounted on a vertical spindle, composed of bonded abrasive grains
- Rotation: Both table and grinding wheel rotate in the same direction
- Material Removal: Controlled removal in passes from 0.0001″ to 0.025″
- Coolant Application: Prevents overheating and flushes debris
- Precision Control: Vertical wheel positioning with accuracies up to ±0.0001″
Here’s a detailed breakdown of the process:
-
Base: A heavy, rigid structure that provides stability and absorbs vibration during grinding.
-
Rotary Table: A rotating table or magnetic chuck securely holds the workpiece in place, especially effective for ferrous materials. It rotates at speeds typically between 10 to 300 RPM, enabling even material exposure.
-
Spindle & Abrasive Wheel: A vertical spindle supports a large, flat grinding wheel composed of bonded abrasive grains. The spindle allows high-speed rotation, often up to 1800 RPM enabling precise, uniform grinding.
-
Wheel Head: This assembly houses the spindle and enables vertical positioning of the grinding wheel. CNC-controlled machines can adjust the wheel’s vertical movement with positioning accuracies of ±0.0001″, allowing for controlled depth cuts from 0.0001″ to 0.025″ per pass.
-
Coolant System: Essential for temperature control and chip removal, the system applies and recirculates coolant, typically water-based emulsions, synthetic fluids, or straight oils directly to the grinding interface.
-
Control System: Manages machine functions, including spindle speed, table rotation, coolant flow, and wheel positioning. CNC models allow for programmable cycles and repeatable precision.
-
Material Removal Process: As the abrasive wheel and rotary table move, often in the same direction—the wheel grinds the surface of the workpiece. This interaction gradually removes material, achieving the desired flatness and finish.
Applications and Industries
Swisher rotary grinders are used across sectors that demand absolute precision:
- Automotive: Engine blocks, transmission parts, rotors, clutch plates
- Aerospace: Turbine blades, landing gear, structural components
- Machine Tools: Guideways, machine beds, fixture bases
- Electronics: Wafer processing, PCB substrates
- Medical Devices: Orthopedic implants, surgical tools
- Others: Foundries, plastics, glass, ceramics
Types of Rotary Grinding Machines
Rotary grinding machines come in various configurations to suit different applications. Here’s a detailed look at the main types:
Vertical Spindle Rotary Surface Grinders
- Features: Large diameter wheel mounted on a vertical spindle
- Best for: Large, flat workpieces
- Advantages: High material removal rates, excellent for roughing operations
- Typical Specifications:
- Table diameters: 24″ to 100″ or larger
- Spindle power: 20 to 100 HP
- Maximum workpiece weight: Up to 10,000 lbs or more
Applications of Vertical Spindle Grinders
- Grinding of large engine blocks in automotive manufacturing
- Processing of heavy steel plates for industrial machinery
- Flattening of large casting surfaces in foundry operations
Double Disc Grinders
- Features: Two opposing grinding wheels
- Best for: Simultaneous grinding of parallel surfaces
- Advantages: High productivity, excellent for thin workpieces
Performance Benefits
- Precision: ±0.0001″ tolerances, 2 microinch finishes
- Efficiency: Up to 20 in³/min removal
- Consistency: Cpk > 1.33 in mass production
- Versatility: Metals, ceramics, composites
- Cost-Effective: Reduced labor and scrap
Choosing the Right Machine for Your Needs
Selecting the appropriate rotary grinding machine depends on several factors:
- Workpiece Size and Shape: Consider the dimensions and geometry of your typical workpieces. This will determine the required table size and machine configuration.
- Material: Different materials may require specific wheel types or grinding parameters.
- Soft materials like aluminum may require silicon carbide wheels
- Hardened steels often benefit from cubic boron nitride (CBN) wheels
- Ceramics may require diamond wheels
- Production Volume: High-volume production may benefit from automated or specialized machines. Consider features like automatic loading/unloading systems and in-process measurement capabilities.
- Precision Requirements: Determine the level of accuracy and surface finish needed for your applications. This will influence the choice of machine type and control system.
- Budget: Consider both initial investment and long-term operational costs.
- Machine purchase price
- Installation and training costs
- Consumables (grinding wheels, coolant)
- Energy consumption
- Maintenance requirements
- Available Space: Ensure you have adequate floor space for the machine and any auxiliary equipment.
- Machine footprint
- Coolant filtration systems
- Material handling equipment
- Operator work areas
Maintenance and Best Practices
To ensure optimal performance and longevity of your rotary grinding machine:
- Regular Inspection: Check for wear on grinding wheels, bearings, and other critical components. Implement a preventive maintenance schedule based on machine usage and manufacturer recommendations.
- Proper Lubrication: Follow manufacturer guidelines for lubricating moving parts. Use high-quality lubricants appropriate for the specific components and operating conditions.
- Coolant Management: Maintain clean coolant and replace it as recommended. Implement a coolant filtration system to remove grinding swarf and maintain coolant quality.
- Wheel Dressing: Regularly dress grinding wheels to maintain their shape and cutting ability. Use precision dressing tools and follow proper dressing techniques to ensure optimal wheel performance.
- Alignment Checks: Periodically verify machine alignment to ensure accuracy. Use precision measurement tools such as electronic levels and laser alignment systems for best results.
Preventive Maintenance Schedule Example
| Frequency | Task |
|---|---|
| Daily | Check coolant level and quality |
| Weekly | Inspect grinding wheel for wear |
| Monthly | Lubricate moving parts |
| Quarterly | Check machine alignment |
| Annually | Overhaul coolant system |
Advancements in Rotary Grinding Technology
The field of rotary grinding continues to evolve with new technologies:
- CNC Integration: Modern machines offer computer numerical control for enhanced precision and automation. Advanced CNC systems provide features such as:
-
- Adaptive control for optimal grinding parameters
- Integrated process monitoring and data logging
- Remote diagnostics and predictive maintenance capabilities
- In-Process Measurement: Advanced sensors allow for real-time monitoring and adjustment during grinding. These systems can measure:
-
- Workpiece dimensions
- Surface finish
- Grinding forces and power consumption
- Superabrasive Wheels: New materials like cubic boron nitride (CBN) offer longer life and better performance. Benefits include:
-
- Higher grinding speeds and material removal rates
- Improved thermal stability for better part quality
- Longer wheel life, reducing downtime for wheel changes
- Eco-Friendly Solutions: Developments in minimum quantity lubrication (MQL) systems reduce coolant usage. These systems:
-
- Minimize environmental impact
- Reduce costs associated with coolant purchase and disposal
- Improve workplace health and safety
| # | Material | Hardness | Part Function | Type of Machine | Rate Stock Removal | Tolerance Thickness | Tolerance Flatness | Surface Finish |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | A-2 | 60Rc | PUNCH | MK VI | .035″ / MIN | 0.0005″ | ±0.0002″ | 20 Ra |
| 2 | A-6 | 62Rc | RACHET RING | ROTARY | .018″ / MIN | ±0.0001″ | ±0.0002″ | 16 Ra |
| 3 | D-2 | 60/62Rc | FORM ROLL DIE | ROTARY | .003″ / MIN | ±0.0003″ | ±0.0003″ | 24 Ra |
| 4 | M-50 | 55Rc | AIRCRAFT BRG | ROTARY | .010 – .020″ / MIN ALL 4 GROUND SURFACES |
±0.0001″ | ±0.00015″ | 8-10 Ra |
| 5 | T-15 | 60/62Rc | FORM TOOL | MK VI | .020″ / MIN | nan | ±0.0002″ | 8-12 Ra |
| 6 | 4140 | 50/55Rc | GEAR BLANK | ROTARY | .070″ / MIN | ±0.0005″ | ±0.0002″ | 24 Ra |
| 7 | P/M | 55Rc | HYO PUMP | AUTO CYCLE ROTARY | COARSE FEED / FINE FEED .050″ – .010″ / MIN |
±0.0001″ | .0001″ | 16 Ra |
| 8 | 8620 | 60Rc | SPUR GEAR | AUTO CYCLE ROTARY | COARSE FEED / FINE FEED .100″ – .020″ / MIN |
±0.0003″ | ±0.0003″ | 24-32 Ra |
| 9 | P/M | 50Rc | HYO PUMP | AUTO CYCLE ROTARY | COARSE FEED / FINE FEED .040″ – .005″ / MIN |
±0.00015″ | ±0.00015″ | 32 Ra |
| 10 | P/M | 50Rc | HYO PUMP | AUTO CYCLE ROTARY | COARSE FEED / FINE FEED .044″ – .005″ / MIN |
±0.00015″ | ±0.00015″ | 32 Ra |
| 11 | CARBIDE | nan | MECHANICAL SEAL | ROTARY | .012″ / MIN | ±0.0002″ | ±0.0002″ | 6-10 Ra |
| 12 | CARBIDE | nan | MECHANICAL SEAL | ROTARY | .002″ / MIN | ±0.0001″ | ±0.0001″ | 0-1 Ra |
| 13 | ALO2 – EPOXY | nan | ELECTRONIC COMP | MK VI | .030″ / MIN | ±0.0005″ | ±0.0005″ | nan |
| 14 | CARBON GRAPHITE | nan | SEAL | MK VI | .080″ / MIN | ±0.0005″ | ±0.0002″ | nan |
| 15 | CERAMIC | nan | DISK | ROTARY | .020″ / MIN 15 PCS / CHUCKLOAD |
±0.0002″ | ±0.0003″ | 8-12 Ra |
| 16 | 1060 | 55/58Rc | BRG END PLATE | ROTARY | .012″ / MIN 25 PCS / CHUCKLOAD |
±0.0003″ | ±0.0005″ | 16-24 Ra |
| 17 | 1018 MAGNETIC STEEL | SOFT | SERVO MOTOR STATOR | ROTARY | .020″ / MIN 8 PCS / CHUCKLOAD |
±0.0002″ | ±0.0002″ | 32 Ra |
| 18 | 430 STAINLESS STEEL | SOFT | ANTO-LOCK BRAKING COMPONENT | ROTARY | .035″ / MIN | ±0.0005″ | ±0.0005″ | 32 Ra |
| 19 | CARBIDE | nan | INSERT | ROTARY | .015″ / MIN 45 PCS / CHUCKLOAD |
±0.0002″ | ±0.0002″ | 8-12 Ra |
| 20 | CARBIDE | nan | INSERT | ROTARY | .001″ / MIN 8 PCS / CHUCKLOAD |
±0.0001″ | ±0.0001″ | 0-1 Ra |
| 21 | BAKELITE | nan | FULE CONTROL SYSTEM | AUTO CYCLE ROTARY | .020″ / MIN 36 PCS / CHUCKLOAD |
±0.0003″ | ±0.0005″ | 32 Ra |